Convolutional Filters and Feature Maps: The Building Blocks of CNNs
A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a type of deep learning artificial neural network specifically designed to process data with a grid-like topology, such as an image. It is composed of multiple layers, including convolutional, activation, pooling, and fully connected layers, that extract features from input data and make predictions through a process called forward propagation.
Convolutional layers apply filters to local regions of the input data, activation layers introduce non-linearity into the network, pooling layers reduce the spatial dimensions of the data, and fully connected layers make the final prediction based on the output from previous layers. CNNs are widely used for image and video recognition, natural language processing, and many other applications.
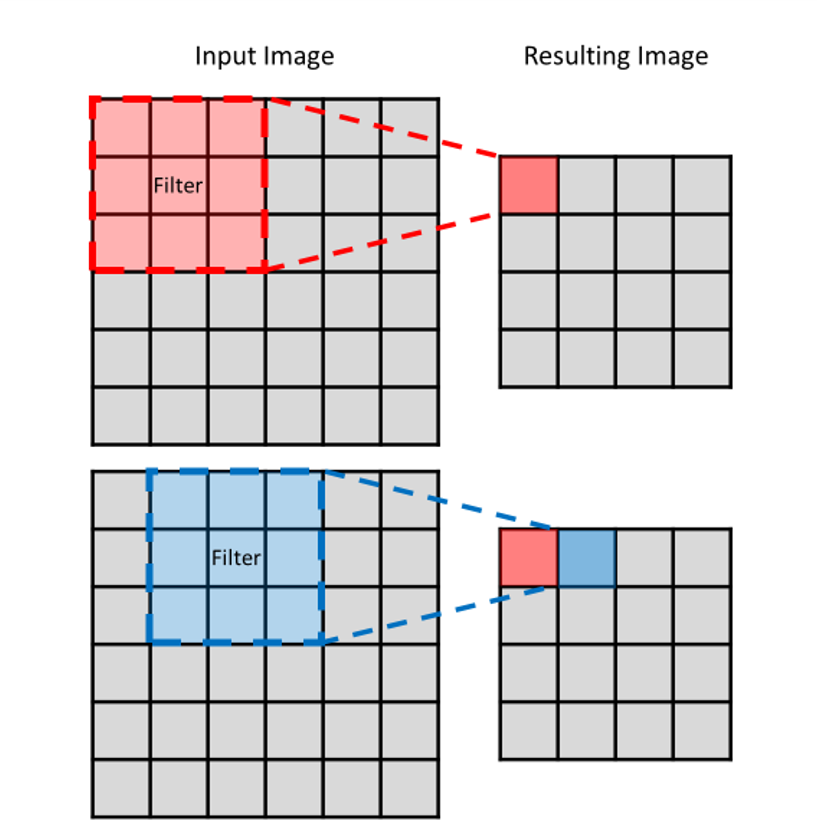
■ What are the Kernel and Filter?
A kernel, also known as a filter in convolutional neural networks (CNNs), is a small matrix of numbers used in the convolution operation. It is designed to detect specific features or patterns in an image. The filter slides across the image, element-wise multiplies the entries of the image with the entries of the filter and then takes the sum, which becomes the output of that convolution operation. The result is a feature map, which highlights the presence of the features detected by the filter.
For example, if the filter is designed to detect edges, it will highlight the image regions with high-intensity gradients (i.e., edges). In a CNN, multiple filters are used in parallel to detect different types of features in the image, and the feature maps generated by these filters are stacked to form the input for the next layer in the network. The weights of the filters are learned during training, making the CNN capable of automatically detecting important features in the image.
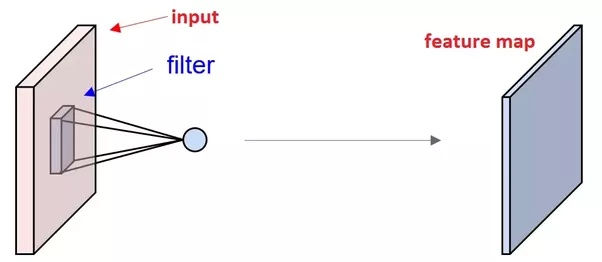
■ What is the feature map?
In a convolutional neural network (CNN), a feature map is the output of a convolution operation between an input image and a filter (also known as a kernel). It is a matrix representing the presence of a specific feature or pattern in the image. The feature map is generated by sliding the filter across the image, element-wise multiplying the entries of the image with the entries of the filter, and taking the sum, which becomes the output of that convolution operation.
An activation map is a feature map passed through an activation function. An activation function is a non-linear function applied to the output of each convolution operation to introduce non-linearity into the network. The purpose of the activation function is to introduce non-linearity into the network, allowing it to model complex relationships between the input and output. The activation function also helps to reduce overfitting by adding some regularization to the model.
For example, the ReLU (rectified linear unit) activation function sets all negative values to zero, effectively suppressing any negative activations in the feature map. This can help to improve the overall performance of the network, as negative activations can hinder the training process. The activation map is used as input for the next layer in the network, and the process of convolution, activation, and pooling is repeated until the final layer is reached.




댓글
댓글 쓰기